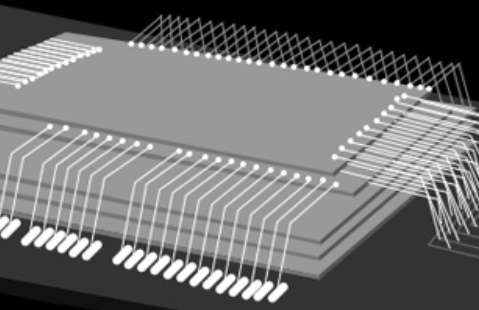
Samsung was developing a new chip packaging technology with its key partners for automotive chips, TheElec has learned.
The tech giant was developing an aluminum oxide (Al2O3) coating bonding wire technology with beefed-up reliability and insulation compared to previous bonding wires, sources said.
Bonding wires connect the I/Os with the lead frame or printed circuit boards.
Most of them in the past have been made with gold (Au) as they are flexible and conductive.
But as gold prices continue to rise, many companies are attempting to mix them with silver (Ag) or copper (Cu).
But these mixed materials usually have weak adhesiveness with their coating materials. This is unacceptable for chips aimed at automobiles as they are exposed to high-temperature and high-humidity environments.
Samsung’s aluminum alternative, which it is developing with Electron, NCD and LT Metal, doesn’t have this weakness.
The aluminum oxide is coated at nanometer thinness onto the metal used as wire.
Aluminum oxide bonds well with insulating coating materials that use epoxy. The precursors used to coat the aluminum oxide such as tri-metal aluminum are also relatively cheap.
Samsung is also planning to use atomic layer deposition to deposit the aluminum oxide as is testing various thicknesses.
However, challenges remain such as off centered ball. Conventionally, a ball is formed at the end of the bonding wire that is attached to the electrode. This ball must be centered right.

